Growth vs. Value Investing: Which Strategy is Right for You?💸💰
Investing for Growth or Value: A Comprehensive Guide 📑
Are you an investor looking to make the most out of your investments? Do you want to understand the differences between growth and value investing and make informed decisions about your portfolio? If so, then keep on reading. In this newsletter, JJ Tax will provide a comprehensive guide on growth investing vs. value investing.
We'll be exploring the pros and cons of each approach, comparing their performance and risks, and providing guidance on when to choose each strategy. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting, this newsletter will help you understand the critical differences between growth and value investing and make informed decisions about your investments. Let's dive into the world of growth investing and value investing!
Growth Investing? Vs. Value Investing?
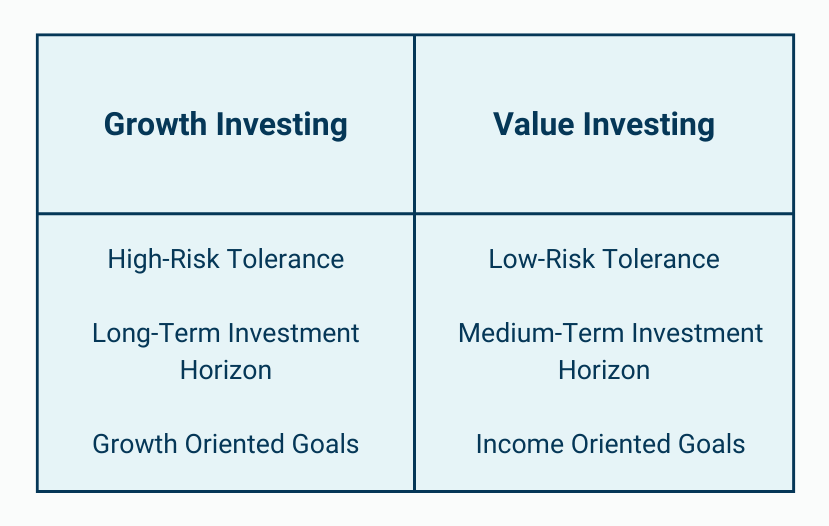
Key Aspects of Growth Investing
Growth investing is a strategy that focuses on companies that have the potential to experience significant growth in revenue, earnings, and cash flow in the future. This approach typically involves investing in companies expanding their market share, developing new products or services, and reinvesting their profits back into their business.
Revenue Growth: Companies with strong revenue growth are often attractive to growth investors. These companies have a track record of increasing their top line, which is a good indicator of their ability to generate revenue in the future.
Earnings Growth: Earnings growth is another important metric for growth investors. Companies that consistently grow their earnings are more likely to be successful in the long term, as they are able to reinvest their profits back into their business and continue to drive growth.
Cash Flow Growth: Cash flow growth is another important metric for growth investors. Companies that generate strong cash flow are better equipped to invest in their business and take advantage of growth opportunities.
Valuation: While growth investors focus on companies with strong growth potential, it is also important to consider valuation. High-growth companies are often priced at a premium, and investors need to ensure that they are not overpaying for growth potential.
Volatility: Growth stocks tend to be more volatile than other stocks, as their growth potential is often tied to market expectations. This means that growth investors need to be comfortable with short-term fluctuations in stock price and have a long-term investment horizon.
Key Aspects of Value Investing
Value investing is a strategy that focuses on identifying companies that are undervalued by the market. This approach typically involves investing in companies with a low price-to-earnings ratio, low price-to-book ratio, or other metrics that suggest the company is trading at a discount to its intrinsic value.
Fundamental Analysis: Value investors rely on fundamental analysis to identify undervalued companies. This involves examining a company's financial statements, earnings, cash flow, and other metrics to determine its intrinsic value.
Margin of Safety: Value investors also focus on the margin of safety, which is the difference between a company's intrinsic value and its market price. By investing in companies with a significant margin of safety, value investors aim to protect themselves against downside risk.
Long-Term Investing: Value investing is a long-term strategy that requires patience and discipline. Value investors typically hold onto their investments for years, if not decades, in order to realize the full potential of their undervalued companies.
Contrarian Thinking: Value investors often go against the market consensus, investing in companies that are out of favor or overlooked by other investors. This contrarian thinking can lead to significant returns if the undervalued company eventually receives recognition from the market.
Qualitative Investing: While value investors focus on undervalued companies, they also pay attention to the quality of the company's business model, management team, and competitive advantages. This is important to ensure that the undervalued company has the potential to deliver sustainable growth over the long term.
When to Choose Growth Investing or Value Investing
Implementing Growth and Value Investing
A roadmap to Growth Investing should involve the following:
Choosing stocks with strong revenue, earnings, and cash flow growth.
Considering metrics like the P/E ratio, PEG ratio, and price-to-sales ratio.
Looking for companies with high growth potential and a competitive advantage in their industry.
A roadmap to Value Investing should involve:
Select undervalued stocks with solid fundamentals.
Consider metrics such as P/B ratio, P/E ratio, and dividend yield.
Look for companies with a strong balance sheet, good management, and consistent earnings growth.
Pay attention to a company's price-to-book and price-to-earnings ratios to identify undervalued opportunities.
Look for companies with a low debt-to-equity ratio, a history of paying dividends, and a low price-to-sales ratio.
Bottom Line
At JJ Tax, we believe that education is key to successful investing. We hope this newsletter has provided valuable insights into the differences between growth and value investing.
Remember, choosing the right investment strategy depends on your personal circumstances and goals. We encourage you to take the time to research and understand the strategies that best align with your investment objectives.
Our team at JJ Tax is always here to help you navigate the complex world of investing and make profitable, informed decisions.
Failed to render LaTeX expression — no expression found